Wenzel 5 and 10 MHz ULN -- Power Supply Sensitivity
We discovered that the Wenzel ULNs are extremely sensitive to external factors, including physical stress and especially noise or variations of the power supply voltage.
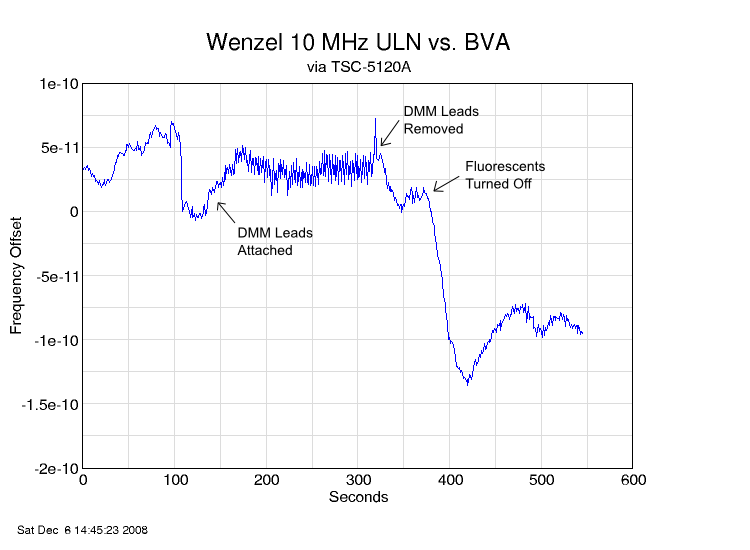
For example, the plot above shows the effect of local disturbances on one of the oscillators. During this data run, I first connected, then disconnected, a pair of DMM leads to the power pins. Then, I turned off the overhead fluorescent lights. The results were pretty noticeable!
To help clean up this noise, I added a stack of bypass capacitors (one each of 0.001uF, 1uF tantalum, and 10uF electrolytic) as close as possible to the power pins of each oscillator.
It's hard to repeat measurements such as the one above, but Allan Deviation plots taken before and after adding the bypass capacitors show quite an improvement (the worsened ADEV at longer tau is due to the fact that the oscillator didn't have as much warm-up time after the caps were added; later experiments verified that the caps had no adverse effect on longer term stability):

To determine the ULN's sensitivity to DC voltage changes, I used an HP 66312A programmable power supply to measure the impact of an increase in the supply voltage from nominally 15.0 to 15.1 volts:

Note that the added filter caps do not make a huge difference in the response.
Given this sensitivity, it may not be too surprising to find that changes even on the far side of a very low noise voltage regulator make a difference.
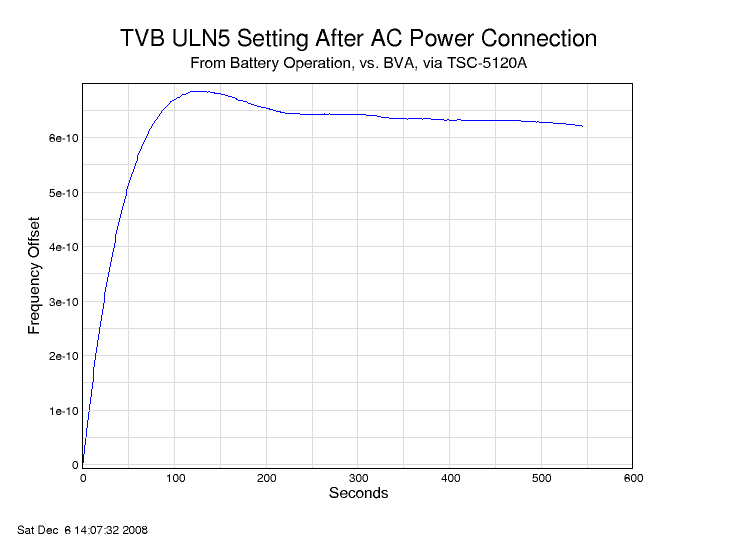
This plot was made with the ULN operating from battery power, through the low noise regulator. The transient is caused by connecting the charging voltage to the battery, increasing the input to the regulator by about 2 volts. The regulator is an ALWSR unit that is based on Walt Jung's "Super Regulator" design and has an LM317T tracking pre-regulator. Despite all that, a change in the input voltage certainly ripples through to the output frequency.
Finally, just for completeness, here is a comparison of operation on battery power, versus operation on battery with the charger connected:

The primary difference is, as one might expect, the reduction of power line spurs at 60 Hertz and harmonics.